LabVIEW Robotics Starter Kit (Robotics Module)
- Updated2023-02-21
- 2 minute(s) read
The NI LabVIEW Robotics Starter Kit includes a robot that runs LabVIEW Robotics software on NI reconfigurable I/O (RIO) hardware. You can use the robot and hardware to prototype and deploy autonomous applications. National Instruments has produced two versions of the Robotics Starter Kit robot, as shown in the following table.
|
|
|
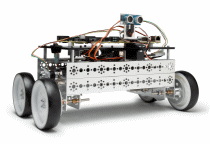
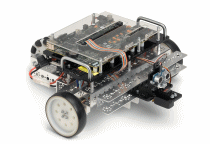
| Starter Kit 1.0 with NI sbRIO-9631 | Starter Kit 2.0 with NI sbRIO-9632 |
|---|
On both robots, the Single-Board RIO (sbRIO) controller, mounted on top of the robot base, includes a real-time processor and Field-Programmable Gate Array (FPGA) on a single board. By default, the FPGA has a sensor and motors wired to digital I/O: a Parallax PING))) ultrasonic distance sensor, a servo motor on which the sensor is mounted, and two DC drive motors. You can expand the built-in analog and digital I/O using C Series modules.
Refer to the National Instruments Web site for more information about the LabVIEW Robotics Starter Kit.
Setting up the Starter Kit Robot
Refer to the printed Quick Start Guide included in the Robotics Starter Kit for information about setting up the Starter Kit robot for the first time. The Quick Start Guide provides instructions for wiring the robot, downloading software to the robot, testing the sensor and motors, and so on.
Required Software for Using the Starter Kit Robot
The Robotics Starter Kit includes a DVD with the LabVIEW Development System and the following LabVIEW add-ons. You must use the media that shipped with your purchase to install all the add-ons on the development computer before you can program a Starter Kit robot.
- LabVIEW Real-Time Module
- LabVIEW FPGA Module
- LabVIEW Robotics Module
- NI-RIO drivers
Programming the Starter Kit Robot
After the development computer, robot, and sbRIO are set up, create a LabVIEW project that contains the Starter Kit hardware targets. Refer to the instructions for programming a Starter Kit robot for more information about controlling the robot in LabVIEW.