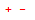Formula Node Syntax
- Updated2026-02-03
- 5 minute(s) read
The Formula Node syntax is similar to the syntax used in text-based programming languages. Remember to end assignments with a semicolon (;) as in C. Use scope rules to declare variables in Formula Nodes. Also, keep in mind the allowed functions and the allowed operators and their precedence in the Formula Node.
The Formula Node syntax is summarized below using Backus-Naur Form (BNF notation). The summary includes non-terminal symbols: compound-statement, identifier, conditional-expression, number, array-size, floating-point-type, integer-type, left-hand-side, assignment-operator, and function. Symbols in red bold monospace are terminal symbols given exactly as they should be reproduced. The symbol # denotes any number of the term following it.





![BNF syntax for array-subscriptions including [assignment] and [assignment] array-subscription.](https://docs-be.ni.com/bundle/labview/page/GUID-98C0CF6B-E10F-451D-A59B-B26C797CE89C-a5.png?_LANG=enus)
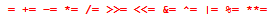

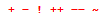



The following table provides the Formula Node syntax for control, conditional, iterative, and switch statements.
| Statement Type | Construct | Grammar | Description/Example |
|---|---|---|---|
| Control Statement | Break Statement |
 |
Use the break keyword to exit the nearest Do, For, or While Loop or switch statement in the Formula Node. |
| Continue Statement |
 |
Use the continue keyword to transfer control to the next iteration of the nearest Do, For, or While Loop in the Formula Node. | |
| Conditional Statement |
 |
if (y==x && a[2][3]<a[0][1]) {
int32 temp;
temp = a[2][3];
a[2][3] = y;
y=temp;
}
else
x=y;
|
|
| If Statement |
 |
||
| If-Else Statement |
 |
||
| Iterative Statement |
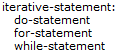 |
||
| Do Loops |
 |
do {
int32 temp;
temp = --a[2]+y;
y=y-1;
}
while (y!=x && a[2]>=a[0]);
|
|
| For Loops |
![BNF syntax for loops including for ( [assignment] ; [assignment] ; [assignment] ) statement.](https://docs-be.ni.com/bundle/labview/page/GUID-A9BE44EB-8BCA-4B4E-83F0-2AB324D086D0-a5.png?_LANG=enus) |
for (y=5; y<x; y*=2) {
int32 temp;
temp = --a[2]+y;
x-=temp;
}
|
|
| While Loops |
 |
while (y!=x && a[2]>=a[0]) {
int32 temp;
temp = --a[2]+y;
y=y-1;
}
|
|
| Switch Statement |
 |
switch(month){
case 2: days = evenyear? 29: 28; break;
case 4:case 6:case9: days = 30; break;
default: days = 31; break;
}
|
|
| Case Statement List |
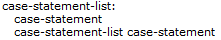 |
||
| Case Statement |
 |

![BNF syntax for array-index-lists including [integer-constant], [integer-constant]array-index-list.](https://docs-be.ni.com/bundle/labview/page/GUID-7CFE3F7A-1772-4B77-9308-8C624A875F0F-a5.png?_LANG=enus)


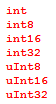






![BNF syntax for identifiers including non-digit [non-first-character].](https://docs-be.ni.com/bundle/labview/page/GUID-9165680F-38ED-4CF7-B427-1C2F8B65A5E7-a5.png?_LANG=enus)
![BNF syntax for non-first-characters including non-digit [non-first-character] and digit [non-first-character].](https://docs-be.ni.com/bundle/labview/page/GUID-54C0B8FF-C4F8-4930-A500-61A533FE48AA-a5.png?_LANG=enus)


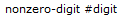
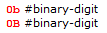



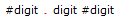
![BNF syntax for exponent-parts including e [sign] #digit and E [sign] #digit.](https://docs-be.ni.com/bundle/labview/page/GUID-A4ED4AF6-1AE5-4571-9B5F-2C767F817337-a5.png?_LANG=enus)