Convert PID Gains
- Updated2025-01-28
- 5 minute(s) read
Converts PID gains in the Academic, Parallel, or Series form to the normalized Parallel form that the PID VI expects.

Inputs/Outputs
 filter coefficient unit (Alpha)
—
filter coefficient unit (Alpha)
—
filter coefficient unit specifies the unit that distinguishes the type of the derivative lowpass filter coefficients.
 filter coefficient (NaN)
—
filter coefficient (NaN)
—
filter coefficient specifies the derivative lowpass filter coefficient. If you specify a value for filter coefficient unit, you must also specify a value for filter coefficient. When filter coefficient unit is Alpha, the valid value range of filter coefficient is [0, 1]. When filter coefficient unit is N, the valid value range of filter coefficient is [1, 1000]. The following equations explain the relationships among the available units: N = 1 / Alpha Time Constant = 1 / (2 * Pi * Cutoff Frequency) When you leave both filter coefficient unit and filter coefficient unwired, this VI uses 0.1 for filter coefficient.  gains pattern (Parallel)
—
gains pattern (Parallel)
—
gains pattern specifies the form of the PD gains.
 proportional
—
proportional
—
proportional specifies the value of the proportional gain.  derivative
—
derivative
—
derivative specifies the value of the derivative gain.  sampling time
—
sampling time
—
sampling time specifies the loop time, in seconds, at which the PID loop on the FPGA target runs.  error in (no error)
—
error in (no error)
—
error in describes error conditions that occur before this node runs. This input provides standard error in functionality.  proportional unit (Gain (K))
—
proportional unit (Gain (K))
—
proportional unit specifies the unit of the proportional gain. The relationship between the available units is K = 100 / PB.
 derivative unit (s)
—
derivative unit (s)
—
derivative unit specifies the units of the derivative gain.
 gains
—
gains
—
gains returns the normalized PD gain parameters.
 error out
—
error out
—
error out contains error information. This output provides standard error out functionality. |
Use the following table to understand the details about the equations that the Convert PID Gains VI uses when converting the PID gains. The converted PID gains are Kp, Ki, and Kd, respectively.
| Original PID Form | Original Gains: Units | Conversion Equations |
|---|---|---|
| Academic | Kc: Gain (K) |





|
| Ti: s | ||
| Td: s | ||
| Parallel | Kp': Gain (K) |


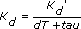


|
| Ki': Hz | ||
| Kd': s | ||
| Series | KC': Gain (K) |





|
| TI': s | ||
| TD': s |
Examples
Refer to the following example files included with LabVIEW FPGA Module.
- labview\examples\CompactRIO\FPGA Fundamentals\FPGA Math and Analysis\Floating-point PID\Multi-Channel PID\Multi-Channel PID.lvproj
- labview\examples\CompactRIO\FPGA Fundamentals\FPGA Math and Analysis\Floating-point PID\Multi-Rate PID\Multi-Rate PID.lvproj
- labview\examples\R Series\FPGA Fundamentals\FPGA Math and Analysis\Floating-point PID\Multi-Channel PID\Multi-Channel PID.lvproj
- labview\examples\R Series\FPGA Fundamentals\FPGA Math and Analysis\Floating-point PID\Multi-Rate PID\Multi-Rate PID.lvproj
 proportional gain
—
proportional gain
—