Zero-Pole-Gain Model Definitions (Advanced Signal Processing Toolkit or Control Design and Simulation Module)
- Updated2023-03-14
- 2 minute(s) read
If you rewrite the equations for the transfer function model to show the locations of the zeros and poles of the dynamic system, you obtain the zero-pole-gain model.
SISO
The following is the equation for the continuous zero-pole-gain SISO model.

| where | s is the Laplace variable and continuous time |
| k is the transfer function gain | |
| Zi are the zeros | |
| Pj are the poles |
The following is the equation for the discrete-time zero-pole-gain SISO model.
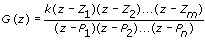
| where | z is discrete time |
When s or z equals 0, you can calculate the static gain from the two equations.

MISO
The following is the equation for the continuous zero-pole-gain MISO model.

| where | Gij are the transfer functions between the stimulus and the response |
| i is the input number of the system | |
| j is the output number of the system |
The following is the equation for the discrete-time zero-pole-gain MISO model.
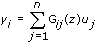
The System Identification VIs do not include a VI to estimate zero-pole-gain models directly because you can use the SI Model Conversion VI to convert another model representation to a zero-pole-gain model.