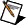SI Model Conversion VI
- Updated2023-03-14
- 3 minute(s) read
SI Model Conversion VI
Owning Palette: Model Conversion VIs
Requires: Advanced Signal Processing Toolkit or Control Design and Simulation Module
Converts a model into another type of model that you can use with the System Identification VIs.
 |
realization type specifies the type of state-space realization to use.
|
||||||
 |
system model in contains information about the model structure, nominal or estimated parameters, identification result, and so on. Use the Model Management VIs to retrieve the information system model in contains.
|
||||||
 |
model type specifies the type of model to which you want to convert system model in.
|
||||||
 |
error in describes error conditions that occur before this node runs. This input provides standard error in functionality. | ||||||
 |
tolerance determines zero-pole cancellations. If the difference between the location of a pole and a zero is within the tolerance, this VI removes the zero-pole pair. You can visually inspect the location difference in the pole-zero plot. The default is 1E-12. | ||||||
 |
system model out returns information about the model structure, nominal or estimated parameters, identification result, and so on. Use the Model Management VIs to retrieve the information system model out contains.
|
||||||
 |
error out contains error information. This output provides standard error out functionality. |
SI Model Conversion Details
You can use this VI to convert an AR, ARX, ARMAX, output-error, Box-Jenkins, or general-linear model into a state-space, transfer function, or zero-pole-gain model; a state-space model into a transfer function or zero-pole-gain model; a transfer function model into a state-space or zero-pole-gain model; and a zero-pole-gain model into a transfer function or state-space model.
Example
Refer to the Model Conversion VI in the labview\examples\System Identification\Getting Started\General.llb for an example of using the SI Model Conversion VI.