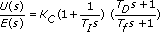PID Function
- Updated2023-03-14
- 8 minute(s) read
Owning Palette: Continuous Linear Systems Functions
Requires: Control Design and Simulation Module
Constructs a PID model in transfer function form.| Dialog Box Options |
| Block Diagram Inputs |
| Block Diagram Outputs |
Dialog Box Options
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Polymorphic instance | Specifies the form this function uses to construct the PID model. You can select Academic, Parallel, or Series. The default is Academic. |
| Parameters | Lists all the parameters associated with this function. Select a parameter from this list to configure the parameter. When you select a parameter, the parameter and its associated Parameter source control appear in the Parameter Information section of the configuration dialog box. |
| Preview | Displays a graphical preview, if available, of the function output or configuration. |
| Parameter Information | Contains the parameters you can configure for this function. You must select a parameter from the Parameters list to make that parameter and its associated Parameter source control visible in the Parameter Information section of the configuration dialog box. |
| Parameter source | Specifies whether you configure this parameter using the Configuration Dialog Box or a Terminal on the simulation diagram. The default value is Configuration Dialog Box. If you select Terminal, LabVIEW displays an input for that parameter on the simulation diagram, and you can wire values to that input to configure this function programmatically. If you select Configuration Dialog Box, LabVIEW removes that input from the simulation diagram. You then must set the value for this parameter inside the configuration dialog box. |
| Proportional Gain (Kc) | Represents the proportional gain of the controller. In the equation that defines the PID Academic form, Kc represents the proportional gain. The default is 1. This option appears if you set Polymorphic instance to Academic. |
| Proportional Gain | Represents the proportional gain of the controller. In the equation that defines the PID Parallel form, KP represents the proportional gain. The default is 1. This option appears if you set Polymorphic instance to Parallel. |
| Proportional Gain (KC) | Represents the proportional gain of the controller. In the equation that defines the PID Series form, KC represents the proportional gain. The default is 1. This option appears if you set Polymorphic instance to Series. |
| Integral time [s] (Ti) | The controller parameter that adjusts the effect of the error integral term E(s)/s on the controller output U(s). In the equation that defines the PID Academic form, Ti represents the integral time. The default is 1. This option appears if you set Polymorphic instance to Academic. |
| Integral Gain | The controller parameter that adjusts the effect of the error integral term E(s)/s on the controller output U(s). In the equation that defines the PID Parallel form, Ki represents the integral gain. The default is 1. This option appears if you set Polymorphic instance to Parallel. |
| Integral Time [s] (TI) | The controller parameter that adjusts the effect of the error integral term E(s)/s on the controller output U(s). In the equation that defines the PID Series form, TI represents the integral time. The default is 1. This option appears if you set Polymorphic instance to Series. |
| Derivative time [s] (Td) | The controller parameter that adjusts the effect of the error derivative term sE(s) on the controller output U(s). In the equation that defines the PID Academic form, Td represents the derivative time. The default is 1. The default PID Academic controller does not use derivative time. This option appears if you set Polymorphic instance to Academic. |
| Derivative Gain | The controller parameter that adjusts the effect of the error derivative term sE(s) on the controller output U(s). In the equation that defines the PID Parallel form, Kd represents the derivative gain. The default is 1. This option appears if you set Polymorphic instance to Parallel. |
| Derivative Time [s] (TD) | The controller parameter that adjusts the effect of the error derivative term sE(s) on the controller output U(s). In the equation that defines the PID Series form, TD represents the derivative time. The default is 1. The default PID Series controller does not use derivative time. This option appears if you set Polymorphic instance to Series. |
| High Frequency [s] (Tf) | The low pass filter time constant Tf this VI uses to make the PID model a proper system. The default is 1. |
| Execution Control | Contains the following options:
|
| Output | Contains the following options:
|
Block Diagram Inputs
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Proportional Gain (Kc) | Represents the proportional gain of the controller. In the equation that defines the PID Academic form, Kc represents the proportional gain. The default is 1. This option appears if you set Polymorphic instance to Academic. |
| Proportional Gain | Represents the proportional gain of the controller. In the equation that defines the PID Parallel form, KP represents the proportional gain. The default is 1. This option appears if you set Polymorphic instance to Parallel. |
| Proportional Gain (KC) | Represents the proportional gain of the controller. In the equation that defines the PID Series form, KC represents the proportional gain. The default is 1. This option appears if you set Polymorphic instance to Series. |
| Integral time [s] (Ti) | The controller parameter that adjusts the effect of the error integral term E(s)/s on the controller output U(s). In the equation that defines the PID Academic form, Ti represents the integral time. The default is 1. This option appears if you set Polymorphic instance to Academic. |
| Integral Gain | The controller parameter that adjusts the effect of the error integral term E(s)/s on the controller output U(s). In the equation that defines the PID Parallel form, Ki represents the integral gain. The default is 1. This option appears if you set Polymorphic instance to Parallel. |
| Integral Time [s] (TI) | The controller parameter that adjusts the effect of the error integral term E(s)/s on the controller output U(s). In the equation that defines the PID Series form, TI represents the integral time. The default is 1. This option appears if you set Polymorphic instance to Series. |
| Derivative time [s] (Td) | The controller parameter that adjusts the effect of the error derivative term sE(s) on the controller output U(s). In the equation that defines the PID Academic form, Td represents the derivative time. The default is 1. The default PID Academic controller does not use derivative time. This option appears if you set Polymorphic instance to Academic. |
| Derivative Gain | The controller parameter that adjusts the effect of the error derivative term sE(s) on the controller output U(s). In the equation that defines the PID Parallel form, Kd represents the derivative gain. The default is 1. This option appears if you set Polymorphic instance to Parallel. |
| Derivative Time [s] (TD) | The controller parameter that adjusts the effect of the error derivative term sE(s) on the controller output U(s). In the equation that defines the PID Series form, TD represents the derivative time. The default is 1. The default PID Series controller does not use derivative time. This option appears if you set Polymorphic instance to Series. |
| High Frequency [s] (Tf) | The low pass filter time constant Tf this VI uses to make the PID model a proper system. The default is 1. |
| Trigger | Specifies the trigger signal the subsystem checks for a zero crossing before executing. In the configuration dialog box, set Execution Control to Trigger or Enable And Trigger to display this input. |
| Enable | Specifies whether the subsystem is enabled. In the configuration dialog box, set Execution Control to Enable or Enable And Trigger to display this input. |
| Error | Specifies the initial value to use for the Output value. The default is 0. |
Block Diagram Outputs
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Output | Returns the result of the calculation from the controller. |
PID Details
This function constructs transfer function models in the following forms:
PID Academic
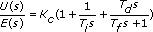
PID Parallel

Refer to the book Digital Control Systems for more information about bilinear-transformation integration.
PID Series