Define PDE Boundary Condition VI
- Updated2025-07-30
- 3 minute(s) read
Defines the boundary condition of partial differential equations. You must manually select the polymorphic instance to use.
The following table gives the definitions of a normal derivative for one-dimensional equations and for two-dimensional equations defined on a rectangular domain.
Note If the boundary type is Neumann, you must specify the value of the normal derivative of the unknown function and not the value of derivatives along the x- or y-axes. Moreover, you cannot specify the Neumann condition on a polygonal domain.
| Position | Normal Derivative (One-Dimension) | Normal Derivative (Rectangular Domain) |
|---|---|---|
| Start X | 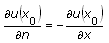 |
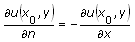 |
| End X | 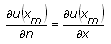 |
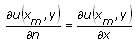 |
| Start Y | N/A | 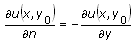 |
| End Y | N/A | 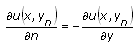 |
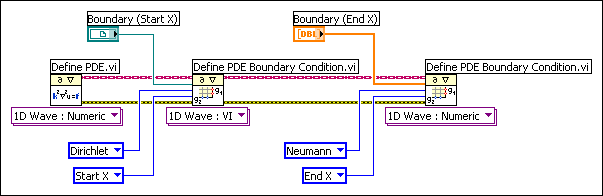
The following block diagram is an example of defining the boundary condition for a one-dimensional wave equation. The boundary condition at Start X is Dirichlet, which the VI defines. The boundary condition at End X is Neumann, which the numeric array defines.
Examples
Refer to the following example files included with LabVIEW.
- labview\examples\Mathematics\Differential Equations - PDE\PDE Flexible Element.vi
- labview\examples\Mathematics\Differential Equations - PDE\PDE String Vibration.vi
- labview\examples\Mathematics\Differential Equations - PDE\PDE Thermal Distribution.vi