TSA Stationarity Test (Array) VI
- Updated2024-07-30
- 4 minute(s) read
Estimates the stationarity of a univariate time series by examining the mean and variance values of the subsequences. Wire data to the Xt input to determine the polymorphic instance to use or manually select the instance.

Inputs/Outputs
 number of segments
—
number of segments
—
number of segments specifies the number of subsequences into which this VI divides the input time series. The default is 100.  Xt
—
Xt
—
Xt specifies the univariate time series.  confidence level (%)
—
confidence level (%)
—
confidence level specifies the level of confidence as a percentage this VI uses to compute the confidence limits of specified statistics value.  error in (no error)
—
error in (no error)
—
error in describes error conditions that occur before this node runs. This input provides standard error in functionality.  stationary
—
stationary
—
stationary returns information about the stationarity of the univariate time series.
 mean of segments
—
mean of segments
—
mean of segments returns the mean value of each subsequence.  variance of segments
—
variance of segments
—
variance of segments returns the variance value of each subsequence.  error out
—
error out
—
error out contains error information. This output provides standard error out functionality. |
TSA Stationarity Test Details
This VI performs stationarity estimation on a univariate time series by testing the inversion number according to the following steps:
1. Divides a time series Xt into l subsequences. The mean value of each subsequence forms a time series m1, m2,…ml. The standard deviation value of each subsequence forms a time series s1, s2,…sl.
2. Computes the sum Sm (Ss) of inversion number for the time series m1, m2,…, ml (s1, s2,…, sl).
If Xt is stationary, the statistical value emes satisfies the normal distribution with a mean value of 0 and a standard deviation value of 1.
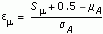
and
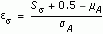
Where mA is the theoretical mean value of Sm or Ss, which equals  , and sA is the theoretical standard deviation value of Sm or Ss, which equals the following equation:
, and sA is the theoretical standard deviation value of Sm or Ss, which equals the following equation:

Given the confidence level a:
- If em<Na/2(0, 1), this time series is mean stationary.
- If es<Na/2(0, 1), this time series is variance stationary.
Examples
Refer to the Series Statistical Analysis VI in the labview\examples\Time Series Analysis\TSAGettingStarted directory for an example of using the TSA Stationarity Test VI.
 mean?
—
mean?
—