Inverse FFT VI
- Updated2023-02-21
- 9 minute(s) read
Inverse FFT VI
Owning Palette: Transforms VIs
Requires: Multicore Analysis and Sparse Matrix Toolkit
Computes the inverse fast Fourier transform (FFT) of the input sequence X.
You must manually select the polymorphic instance you want to use.
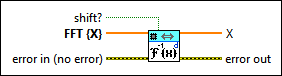
1D Inverse FFT (DBL)
 |
shift? specifies whether the DC component is at the center of FFT {X}. The default is FALSE. |
 |
FFT {X} specifies the complex-valued input sequence, which should be conjugated centrosymmetric except for the first element. |
 |
error in describes error conditions that occur before this node runs. This input provides standard error in functionality. |
 |
X returns the inverse FFT of FFT {X}. |
 |
error out contains error information. This output provides standard error out functionality. |
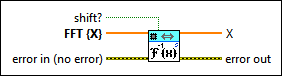
1D Inverse FFT (SGL)
 |
shift? specifies whether the DC component is at the center of FFT {X}. The default is FALSE. |
 |
FFT {X} specifies the complex-valued input sequence, which should be conjugated centrosymmetric except for the first element. |
 |
error in describes error conditions that occur before this node runs. This input provides standard error in functionality. |
 |
X returns the inverse FFT of FFT {X}. |
 |
error out contains error information. This output provides standard error out functionality. |
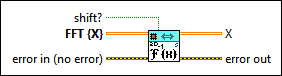
2D Inverse FFT (SGL)
 |
shift? specifies whether the DC component is at the center of FFT {X}. The default is FALSE. |
 |
FFT {X} specifies the complex-valued input sequence, which should be conjugated centrosymmetric except for the first row and column. |
 |
error in describes error conditions that occur before this node runs. This input provides standard error in functionality. |
 |
X returns the inverse FFT of FFT {X}. |
 |
error out contains error information. This output provides standard error out functionality. |
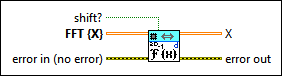
2D Inverse FFT (DBL)
 |
shift? specifies whether the DC component is at the center of FFT {X}. The default is FALSE. |
 |
FFT {X} specifies the complex-valued input sequence, which should be conjugated centrosymmetric except for the first row and column. |
 |
error in describes error conditions that occur before this node runs. This input provides standard error in functionality. |
 |
X returns the inverse FFT of FFT {X}. |
 |
error out contains error information. This output provides standard error out functionality. |
1D Inverse FFT (CSG)
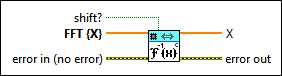
 |
shift? specifies whether the DC component is at the center of FFT {X}. The default is FALSE. |
 |
FFT {X} specifies the complex-valued input sequence. |
 |
error in describes error conditions that occur before this node runs. This input provides standard error in functionality. |
 |
X returns the inverse FFT of FFT {X}. |
 |
error out contains error information. This output provides standard error out functionality. |
1D Inverse FFT (CDB)
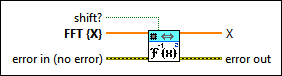
 |
shift? specifies whether the DC component is at the center of FFT {X}. The default is FALSE. |
 |
FFT {X} specifies the complex-valued input sequence. |
 |
error in describes error conditions that occur before this node runs. This input provides standard error in functionality. |
 |
X returns the inverse FFT of FFT {X}. |
 |
error out contains error information. This output provides standard error out functionality. |
3D Inverse FFT (SGL)
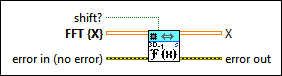
 |
shift? specifies whether the DC component is at the center of FFT {X}. The default is FALSE. |
 |
FFT {X} specifies the complex-valued input sequence, which should be conjugated centrosymmetric. |
 |
error in describes error conditions that occur before this node runs. This input provides standard error in functionality. |
 |
X returns the inverse FFT of FFT {X}. |
 |
error out contains error information. This output provides standard error out functionality. |
3D Inverse FFT (DBL)
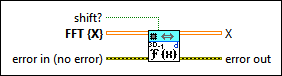
 |
shift? specifies whether the DC component is at the center of FFT {X}. The default is FALSE. |
 |
FFT {X} specifies the complex-valued input sequence, which should be conjugated centrosymmetric. |
 |
error in describes error conditions that occur before this node runs. This input provides standard error in functionality. |
 |
X returns the inverse FFT of FFT {X}. |
 |
error out contains error information. This output provides standard error out functionality. |
2D Inverse FFT (CSG)
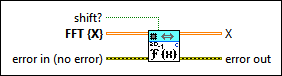
 |
shift? specifies whether the DC component is at the center of FFT {X}. The default is FALSE. |
 |
FFT {X} specifies the complex-valued input sequence. |
 |
error in describes error conditions that occur before this node runs. This input provides standard error in functionality. |
 |
X returns the inverse FFT of FFT {X}. |
 |
error out contains error information. This output provides standard error out functionality. |
2D Inverse FFT (CDB)
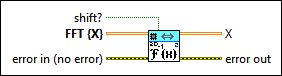
 |
shift? specifies whether the DC component is at the center of FFT {X}. The default is FALSE. |
 |
FFT {X} specifies the complex-valued input sequence. |
 |
error in describes error conditions that occur before this node runs. This input provides standard error in functionality. |
 |
X returns the inverse FFT of FFT {X}. |
 |
error out contains error information. This output provides standard error out functionality. |
3D Inverse FFT (CDB)
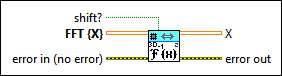
 |
shift? specifies whether the DC component is at the center of FFT {X}. The default is FALSE. |
 |
FFT {X} specifies the complex-valued input sequence. |
 |
error in describes error conditions that occur before this node runs. This input provides standard error in functionality. |
 |
X returns the inverse FFT of FFT {X}. |
 |
error out contains error information. This output provides standard error out functionality. |
3D Inverse FFT (CSG)
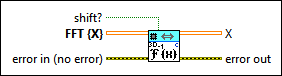
 |
shift? specifies whether the DC component is at the center of FFT {X}. The default is FALSE. |
 |
FFT {X} specifies the complex-valued input sequence. |
 |
error in describes error conditions that occur before this node runs. This input provides standard error in functionality. |
 |
X returns the inverse FFT of FFT {X}. |
 |
error out contains error information. This output provides standard error out functionality. |
Inverse FFT Details
The following table lists the support characteristics of this VI.
| Supported on RT targets | Yes |
| Suitable for bounded execution times on RT | Yes |
Use the DBL or SGL instance of this VI only if FFT {X} is the Fourier transform of a real time-domain signal. Otherwise, use the CDB or CSG instance.
For a 1D, N-sample, frequency domain sequence Y, the following equation defines the inverse discrete Fourier transform (IDFT):
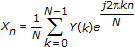
for n=0, 1, …, N–1.
For a 2D, M-by-N frequency domain sequence Y, the following equation defines the inverse discrete Fourier transform (IDFT):
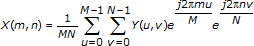
for m = 0, 1, …, M–1, n=0, 1, …, N–1.
For a 3D, M-by-N-by-K frequency domain sequence Y, the following equation defines the inverse discrete Fourier transform (IDFT):
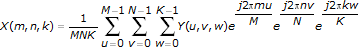
for m = 0, 1, …, M–1, n=0, 1, …, N–1, k=0, 1, …, K–1.