Graphs and Sparse Matrices (Multicore Analysis and Sparse Matrix Toolkit)
- Updated2023-02-21
- 2 minute(s) read
Graphs and graph theory, the study of graphs, are widely used in computer science, biology, material science, sociology, and so on. A graph is an abstract representation of a set of vertices connected by edges. The set of vertices is usually numbered from 0 to n-1, where n is the total number of vertices. The method of numbering the vertices is not unique. If the graph does not distinguish between the edges from vertices i to j and j to i, the graph is an undirected graph. Otherwise, the graph is a directed graph.
A matrix can represent a graph and vice versa. Therefore, you can use matrix theory and matrix operations to solve graph problems, such as graph partition. Graphs also play an important role in sparse matrix analysis. You use graph theory in solving the system of sparse linear equations, especially in determining the reordering strategy.
The n-by-n adjacent matrix is the most typical matrix representation of a graph on n vertices. The matrix element on the (i, j) position associates with the graph edge from vertices i to j. A zero matrix element usually means that there is no connection between corresponding vertices. The adjacent matrix is symmetric if the graph is an undirected one. Otherwise, the adjacent matrix can be non-symmetric. For example, the following figure shows a graph with seven vertices and 11 edges.
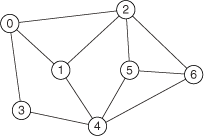
Suppose that the edges in the graph are undirected and not weighted. The following symmetric matrix represents the corresponding adjacent matrix.
