Model-View-Controller Design Pattern
- Updated2025-11-07
- 2 minute(s) read
The Model-View-Controller (MVC) design pattern is an application design pattern that consists of three components: a model represents any data in the system, a view provides access to the model, and a controller processes events and then updates the model with new data.
The following flowchart illustrates the interaction of each component in the MVC design pattern:

As shown in the previous flowchart, when an event occurs in a system, the system passes the event to a controller that monitors the event. The controller processes the event and then updates the model. Views receive data changes from the model and update accordingly.
You can use the MVC design pattern for most LabVIEW Datalogging and Supervisory Control (DSC) Module applications. In the DSC Module, shared variables and other I/O points represent a model. A set of front panel windows represents a view. Front panel windows interact with the model through front panel data binding. Any supervisory program, such as an I/O server, running in the application represents a controller.
The following flowchart illustrates the interaction of the components in a DSC Module application according to the MVC design pattern:
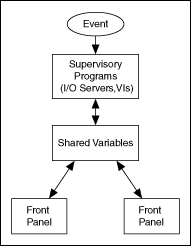
The DSC Module is an event-driven I/O system. Real-world sensor inputs or user inputs through a front panel can generate events. When an event occurs, the Shared Variable Engine processes and passes the event to any supervisory programs that monitor the event. Then the DSC Module either executes these supervisory programs and updates the shared variables or directly passes the event to the shared variables. Front panel windows interact with the shared variables through front panel data binding and update accordingly when data changes.
When you develop a DSC Module application, you can build a model, a view, and a controller in any order. However, the manufacturer recommends that you build an application in the following order:
- Design a model. Define how you want to organize shared variables in the application. Create a project and use LabVIEW project libraries to organize functional groups of shared variables.
- Design a view. Create front panel windows to interact with the shared variables.
- Design one or more controllers. Create supervisory control VIs that process events in the application.