SI Recursively Estimate ARX Model VI
- Updated2023-03-14
- 15 minute(s) read
SI Recursively Estimate ARX Model VI
Owning Palette: Recursive Model Estimation VIs
Requires: Advanced Signal Processing Toolkit or Control Design and Simulation Module
Estimates the parameters of an ARX model using a recursive method. Wire data to the stimulus signal and response signal inputs to determine the polymorphic instance to use or manually select the instance.
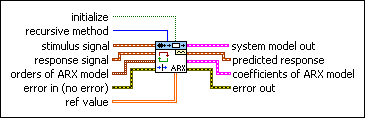
SI Recursively Estimate ARX Model (SISO Waveform)
 |
initialize specifies whether to initialize the internal state of the VI. This VI performs calculations that are dependent on all previous data since you last ran the VI or since you set initialize to TRUE. When initialize is TRUE, this VI restarts the calculation dependency. The default is FALSE. | ||||||||
 |
recursive method specifies the recursive estimation method to use.
|
||||||||
 |
stimulus signal specifies the input waveform of the stimulus signal. | ||||||||
 |
response signal specifies the input waveform of the response signal. | ||||||||
 |
orders of ARX model specifies the orders and delay of the ARX model.
| ||||||||
 |
error in describes error conditions that occur before this node runs. This input provides standard error in functionality. | ||||||||
 |
ref value specifies the reference value for the recursive estimation algorithms. When recursive method is KF, ref value is the drift matrix. This method uses the drift matrix to prevent the gradient from approaching zero in the identification process. The gradient indicates the changes of the model coefficients. When recursive method is RLS, this VI uses the value in the first row and the first column of ref value as the forgetting factor. The forgetting factor specifies the percentage of information this VI uses from previous estimation calculations. The range of the forgetting factor is between 0 and 1. For example, if you set the forgetting factor to 0.5, this VI uses 50% of information from previous estimation. If you want to estimate a time-invariant system, you can set the forgetting factor between 0.98 and less than 1. If you want to estimate a time-variant system, you can set a smaller forgetting factor. Then, this VI can have a better ability to track the changes of the system coefficients. When recursive method is NLMS or LMS, this VI uses the value in the first row and the first column of ref value as the step size. The value of the step size is proportional to the convergence rate. The larger the step size, the faster the convergence. However, the algorithm can become unstable if the step size gets too large. An appropriate step size depends on the model type, order, and input signal. |
||||||||
 |
system model out returns information about the model structure, nominal or estimated parameters, identification result, and so on. Use the Model Management VIs to retrieve the information system model out contains.
|
||||||||
 |
predicted response returns the predicted response output from the current estimated system model. The difference between the values of predicted response and response signal is the measure of the recursive estimation. | ||||||||
 |
coefficients of ARX model returns the coefficients of the ARX model.
| ||||||||
 |
error out contains error information. This output provides standard error out functionality. |
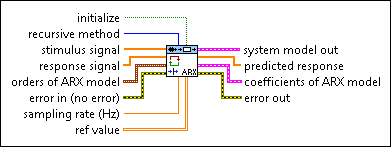
SI Recursively Estimate ARX Model (SISO Array)
 |
initialize specifies whether to initialize the internal state of the VI. This VI performs calculations that are dependent on all previous data since you last ran the VI or since you set initialize to TRUE. When initialize is TRUE, this VI restarts the calculation dependency. The default is FALSE. | ||||||||
 |
recursive method specifies the recursive estimation method to use.
|
||||||||
 |
stimulus signal specifies an array that represents the stimulus signal. | ||||||||
 |
response signal specifies an array that represents the response signal. | ||||||||
 |
orders of ARX model specifies the orders and delay of the ARX model.
| ||||||||
 |
error in describes error conditions that occur before this node runs. This input provides standard error in functionality. | ||||||||
 |
sampling rate (Hz) is the signal sampling rate in hertz. The value of sampling rate must be greater than 0. | ||||||||
 |
ref value specifies the reference value for the recursive estimation algorithms. When recursive method is KF, ref value is the drift matrix. This method uses the drift matrix to prevent the gradient from approaching zero in the identification process. The gradient indicates the changes of the model coefficients. When recursive method is RLS, this VI uses the value in the first row and the first column of ref value as the forgetting factor. The forgetting factor specifies the percentage of information this VI uses from previous estimation calculations. The range of the forgetting factor is between 0 and 1. For example, if you set the forgetting factor to 0.5, this VI uses 50% of information from previous estimation. If you want to estimate a time-invariant system, you can set the forgetting factor between 0.98 and less than 1. If you want to estimate a time-variant system, you can set a smaller forgetting factor. Then, this VI can have a better ability to track the changes of the system coefficients. When recursive method is NLMS or LMS, this VI uses the value in the first row and the first column of ref value as the step size. The value of the step size is proportional to the convergence rate. The larger the step size, the faster the convergence. However, the algorithm can become unstable if the step size gets too large. An appropriate step size depends on the model type, order, and input signal. |
||||||||
 |
system model out returns information about the model structure, nominal or estimated parameters, identification result, and so on. Use the Model Management VIs to retrieve the information system model out contains.
|
||||||||
 |
predicted response returns the predicted response output from the current estimated system model. The difference between the values of predicted response and response signal is the measure of the recursive estimation. | ||||||||
 |
coefficients of ARX model returns the coefficients of the ARX model.
| ||||||||
 |
error out contains error information. This output provides standard error out functionality. |
SI Recursively Estimate ARX Model (MISO Waveform)

 |
initialize specifies whether to initialize the internal state of the VI. This VI performs calculations that are dependent on all previous data since you last ran the VI or since you set initialize to TRUE. When initialize is TRUE, this VI restarts the calculation dependency. The default is FALSE. | ||||||||
 |
recursive method specifies the recursive estimation method to use.
|
||||||||
 |
stimulus signals specifies the input waveform array of the stimulus signals. Each element of the array is the waveform of one stimulus signal. | ||||||||
 |
response signal specifies the input waveform of the response signal. | ||||||||
 |
orders of ARX model specifies the orders and delays of the ARX model.
| ||||||||
 |
error in describes error conditions that occur before this node runs. This input provides standard error in functionality. | ||||||||
 |
ref value specifies the reference value for the recursive estimation algorithms. When recursive method is KF, ref value is the drift matrix. This method uses the drift matrix to prevent the gradient from approaching zero in the identification process. The gradient indicates the changes of the model coefficients. When recursive method is RLS, this VI uses the value in the first row and the first column of ref value as the forgetting factor. The forgetting factor specifies the percentage of information this VI uses from previous estimation calculations. The range of the forgetting factor is between 0 and 1. For example, if you set the forgetting factor to 0.5, this VI uses 50% of information from previous estimation. If you want to estimate a time-invariant system, you can set the forgetting factor between 0.98 and less than 1. If you want to estimate a time-variant system, you can set a smaller forgetting factor. Then, this VI can have a better ability to track the changes of the system coefficients. When recursive method is NLMS or LMS, this VI uses the value in the first row and the first column of ref value as the step size. The value of the step size is proportional to the convergence rate. The larger the step size, the faster the convergence. However, the algorithm can become unstable if the step size gets too large. An appropriate step size depends on the model type, order, and input signal. |
||||||||
 |
system model out returns information about the model structure, nominal or estimated parameters, identification result, and so on. Use the Model Management VIs to retrieve the information system model out contains.
|
||||||||
 |
predicted response returns the predicted response output from the current estimated system model. The difference between the values of predicted response and response signal is the measure of the recursive estimation. | ||||||||
 |
coefficients of ARX model returns the coefficients of the ARX model.
| ||||||||
 |
error out contains error information. This output provides standard error out functionality. |
SI Recursively Estimate ARX Model (MISO Array)

 |
initialize specifies whether to initialize the internal state of the VI. This VI performs calculations that are dependent on all previous data since you last ran the VI or since you set initialize to TRUE. When initialize is TRUE, this VI restarts the calculation dependency. The default is FALSE. | ||||||||
 |
recursive method specifies the recursive estimation method to use.
|
||||||||
 |
stimulus signals specifies an array that represents the stimulus signals. Each row in the array is one stimulus signal. | ||||||||
 |
response signal specifies an array that represents the response signal. Each row in the array is one response signal. | ||||||||
 |
orders of ARX model specifies the orders and delays of the ARX model.
| ||||||||
 |
error in describes error conditions that occur before this node runs. This input provides standard error in functionality. | ||||||||
 |
sampling rate (Hz) is the signal sampling rate in hertz. The value of sampling rate must be greater than 0. | ||||||||
 |
ref value specifies the reference value for the recursive estimation algorithms. When recursive method is KF, ref value is the drift matrix. This method uses the drift matrix to prevent the gradient from approaching zero in the identification process. The gradient indicates the changes of the model coefficients. When recursive method is RLS, this VI uses the value in the first row and the first column of ref value as the forgetting factor. The forgetting factor specifies the percentage of information this VI uses from previous estimation calculations. The range of the forgetting factor is between 0 and 1. For example, if you set the forgetting factor to 0.5, this VI uses 50% of information from previous estimation. If you want to estimate a time-invariant system, you can set the forgetting factor between 0.98 and less than 1. If you want to estimate a time-variant system, you can set a smaller forgetting factor. Then, this VI can have a better ability to track the changes of the system coefficients. When recursive method is NLMS or LMS, this VI uses the value in the first row and the first column of ref value as the step size. The value of the step size is proportional to the convergence rate. The larger the step size, the faster the convergence. However, the algorithm can become unstable if the step size gets too large. An appropriate step size depends on the model type, order, and input signal. |
||||||||
 |
system model out returns information about the model structure, nominal or estimated parameters, identification result, and so on. Use the Model Management VIs to retrieve the information system model out contains.
|
||||||||
 |
predicted response returns the predicted response output from the current estimated system model. The difference between the values of predicted response and response signal is the measure of the recursive estimation. | ||||||||
 |
coefficients of ARX model returns the coefficients of the ARX model.
| ||||||||
 |
error out contains error information. This output provides standard error out functionality. |
Example
Refer to the Online Model Estimation VI in the labview\examples\System Identification\Getting Started\Recursive Estimation.llb for an example of using the SI Recursively Estimate ARX Model VI.