SI Create Partially Known State-Space Model VI
- Updated2023-03-14
- 17 minute(s) read
SI Create Partially Known State-Space Model VI
Owning Palette: Partially Known Model Estimation VIs
Requires: Advanced Signal Processing Toolkit or Control Design and Simulation Module
Creates a state-space model for a partially known system. Use the SI Estimate Partially Known State-Space Model VI to estimate the model you create with this VI. You must manually select the polymorphic instance to use.
SI Create Partially Known State-Space Model (Continuous SISO)

 |
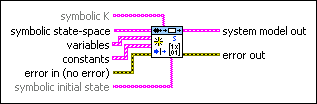
symbolic K specifies the symbolic representation of the Kalman gain. If symbolic K is not provided, the estimated state-space model contains only the deterministic part of the system. | ||||||||
 |
symbolic state-space specifies the matrices of a state-space model in symbolic representation.
| ||||||||
 |
variables specifies the names and values of the variables in the state-space model.
| ||||||||
 |
constants specifies the names and values of the constants in the state-space model.
| ||||||||
 |
error in describes error conditions that occur before this node runs. This input provides standard error in functionality. | ||||||||
 |
symbolic initial state is the symbolic representation of the initial state. | ||||||||
 |
system model out returns information about the model structure, nominal or estimated parameters, identification result, and so on. | ||||||||
 |
error out contains error information. This output provides standard error out functionality. |
SI Create Partially Known State-Space Model (Continuous MISO)
 |
symbolic K specifies the symbolic representation of the Kalman gain. If symbolic K is not provided, the estimated state-space model contains only the deterministic part of the system. | ||||||||
 |
symbolic state-space specifies the matrices of a state-space model in symbolic representation.
| ||||||||
 |
variables specifies the names and values of the variables in the state-space model.
| ||||||||
 |
constants specifies the names and values of the constants in the state-space model.
| ||||||||
 |
error in describes error conditions that occur before this node runs. This input provides standard error in functionality. | ||||||||
 |
symbolic initial state is the symbolic representation of the initial state. | ||||||||
 |
system model out returns information about the model structure, nominal or estimated parameters, identification result, and so on. | ||||||||
 |
error out contains error information. This output provides standard error out functionality. |
SI Create Partially Known State-Space Model (Continuous MIMO)

 |
symbolic K is the symbolic representation of the Kalman gain. If symbolic K is not provided, the estimated state-space model contains only the deterministic part of the system. | ||||||||
 |
symbolic state-space specifies the matrices of a state-space model in symbolic representation.
| ||||||||
 |
variables specifies the names and values of the variables in the state-space model.
| ||||||||
 |
constants specifies the names and values of the constants in the state-space model.
| ||||||||
 |
error in describes error conditions that occur before this node runs. This input provides standard error in functionality. | ||||||||
 |
symbolic initial state is the symbolic representation of the initial state. | ||||||||
 |
system model out returns information about the model structure, nominal or estimated parameters, identification result, and so on. | ||||||||
 |
error out contains error information. This output provides standard error out functionality. |
SI Create Partially Known State-Space Model (Discrete SISO)

 |
symbolic K specifies the symbolic representation of the Kalman gain. If symbolic K is not provided, the estimated state-space model contains only the deterministic part of the system. | ||||||||
 |
symbolic state-space specifies the matrices of a state-space model in symbolic representation.
| ||||||||
 |
variables specifies the names and values of the variables in the state-space model.
| ||||||||
 |
constants specifies the names and values of the constants in the state-space model.
| ||||||||
 |
error in describes error conditions that occur before this node runs. This input provides standard error in functionality. | ||||||||
 |
sampling rate (Hz) is the signal sampling rate in hertz. The value of sampling rate must be greater than 0. | ||||||||
 |
symbolic initial state is the symbolic representation of the initial state. | ||||||||
 |
system model out returns information about the model structure, nominal or estimated parameters, identification result, and so on. | ||||||||
 |
error out contains error information. This output provides standard error out functionality. |
SI Create Partially Known State-Space Model (Discrete MISO)

 |
symbolic K specifies the symbolic representation of the Kalman gain. If symbolic K is not provided, the estimated state-space model contains only the deterministic part of the system. | ||||||||
 |
symbolic state-space specifies the matrices of a state-space model in symbolic representation.
| ||||||||
 |
variables specifies the names and values of the variables in the state-space model.
| ||||||||
 |
constants specifies the names and values of the constants in the state-space model.
| ||||||||
 |
error in describes error conditions that occur before this node runs. This input provides standard error in functionality. | ||||||||
 |
sampling rate (Hz) is the signal sampling rate in hertz. The value of sampling rate must be greater than 0. | ||||||||
 |
symbolic initial state is the symbolic representation of the initial state. | ||||||||
 |
system model out returns information about the model structure, nominal or estimated parameters, identification result, and so on. | ||||||||
 |
error out contains error information. This output provides standard error out functionality. |
SI Create Partially Known State-Space Model (Discrete MIMO)

 |
symbolic K is the symbolic representation of the Kalman gain. If symbolic K is not provided, the estimated state-space model contains only the deterministic part of the system. | ||||||||
 |
symbolic state-space specifies the matrices of a state-space model in symbolic representation.
| ||||||||
 |
variables specifies the names and values of the variables in the state-space model.
| ||||||||
 |
constants specifies the names and values of the constants in the state-space model.
| ||||||||
 |
error in describes error conditions that occur before this node runs. This input provides standard error in functionality. | ||||||||
 |
sampling rate (Hz) is the signal sampling rate in hertz. The value of sampling rate must be greater than 0. | ||||||||
 |
symbolic initial state is the symbolic representation of the initial state. | ||||||||
 |
system model out returns information about the model structure, nominal or estimated parameters, identification result, and so on. | ||||||||
 |
error out contains error information. This output provides standard error out functionality. |
Examples
Refer to the following VIs for examples of using the SI Create Partially Known State-Space Model VI:
- Continuous State-Space Model of an RLC Circuit VI: labview\examples\System Identification\Getting Started\Grey-Box Model.llb
- Belt-driven Motion System (Greybox) VI: labview\examples\System Identification\Industry Applications\Mechanical Systems.llb
