CD Subtract Models VI
- Updated2023-03-14
- 9 minute(s) read
CD Subtract Models VI
Owning Palette: Model Interconnection VIs
Requires: Control Design and Simulation Module
Subtracts linear models. This VI subtracts Model 2 from Model 1. You also can subtract a single-input single-output (SISO) model or a constant gain from each element of a multiple-input multiple-output (MIMO) model and vice-versa. The models either must be continuous-time models or must have the same sampling time if they are discrete-time models. Wire data to the Model 1 and Model 2 inputs to determine the polymorphic instance to use or manually select the instance.
CD Subtract Models (State-Space from State-Space)

 |
Model 1 specifies the first model this VI uses to create the Model Out. |
 |
Model 2 specifies the second model this VI uses to create the Model Out. |
 |
error in describes error conditions that occur before this node runs. This input provides standard error in functionality. |
 |
Model Out returns the model this VI produces. When the two input models are not of the same model type, the following model hierarchy determines the model type of the resulting model: state-space>transfer function>zero-pole-gain. For example, if one input is a state-space model and the other is a zero-pole-gain model, the resulting model is a state-space model. To access and modify the data in the model, use the Model Information VIs. |
 |
error out contains error information. This output provides standard error out functionality. |
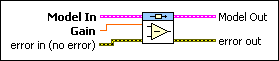
CD Subtract Models (Gain from State-Space)
 |
Model In specifies the model from which you want to subtract information. |
 |
Gain specifies the gain to subtract from the model. |
 |
error in describes error conditions that occur before this node runs. This input provides standard error in functionality. |
 |
Model Out returns the model this VI produces. When the two input models are not of the same model type, the following model hierarchy determines the model type of the resulting model: state-space>transfer function>zero-pole-gain. For example, if one input is a state-space model and the other is a zero-pole-gain model, the resulting model is a state-space model. To access and modify the data in the model, use the Model Information VIs. |
 |
error out contains error information. This output provides standard error out functionality. |
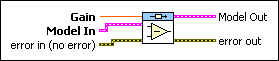
CD Subtract Models (State-Space from Gain)
 |
Gain specifies the gain from which this VI subtracts the model. |
 |
Model In specifies the model this VI subtracts from the gain. |
 |
error in describes error conditions that occur before this node runs. This input provides standard error in functionality. |
 |
Model Out returns the model this VI produces. When the two input models are not of the same model type, the following model hierarchy determines the model type of the resulting model: state-space>transfer function>zero-pole-gain. For example, if one input is a state-space model and the other is a zero-pole-gain model, the resulting model is a state-space model. To access and modify the data in the model, use the Model Information VIs. |
 |
error out contains error information. This output provides standard error out functionality. |
CD Subtract Models (Transfer Function from Transfer Function)

 |
Model 1 specifies the first model this VI uses to create the Model Out. |
 |
Model 2 specifies the second model this VI uses to create the Model Out. |
 |
error in describes error conditions that occur before this node runs. This input provides standard error in functionality. |
 |
Model Out returns the model this VI produces. When the two input models are not of the same model type, the following model hierarchy determines the model type of the resulting model: state-space>transfer function>zero-pole-gain. For example, if one input is a state-space model and the other is a zero-pole-gain model, the resulting model is a state-space model. To access and modify the data in the model, use the Model Information VIs. |
 |
error out contains error information. This output provides standard error out functionality. |
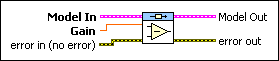
CD Subtract Models (Gain from Transfer Function)
 |
Model In specifies the model from which you want to subtract information. |
 |
Gain specifies the gain to subtract from the model. |
 |
error in describes error conditions that occur before this node runs. This input provides standard error in functionality. |
 |
Model Out returns the model this VI produces. When the two input models are not of the same model type, the following model hierarchy determines the model type of the resulting model: state-space>transfer function>zero-pole-gain. For example, if one input is a state-space model and the other is a zero-pole-gain model, the resulting model is a state-space model. To access and modify the data in the model, use the Model Information VIs. |
 |
error out contains error information. This output provides standard error out functionality. |
CD Subtract Models (Transfer Function from Gain)

 |
Gain specifies the gain from which this VI subtracts the model. |
 |
Model In specifies the model this VI subtracts from the gain. |
 |
error in describes error conditions that occur before this node runs. This input provides standard error in functionality. |
 |
Model Out returns the model this VI produces. When the two input models are not of the same model type, the following model hierarchy determines the model type of the resulting model: state-space>transfer function>zero-pole-gain. For example, if one input is a state-space model and the other is a zero-pole-gain model, the resulting model is a state-space model. To access and modify the data in the model, use the Model Information VIs. |
 |
error out contains error information. This output provides standard error out functionality. |
CD Subtract Models (Zero-Pole-Gain from Zero-Pole-Gain)

 |
Model 1 specifies the first model this VI uses to create the Model Out. |
 |
Model 2 specifies the second model this VI uses to create the Model Out. |
 |
error in describes error conditions that occur before this node runs. This input provides standard error in functionality. |
 |
Model Out returns the model this VI produces. When the two input models are not of the same model type, the following model hierarchy determines the model type of the resulting model: state-space>transfer function>zero-pole-gain. For example, if one input is a state-space model and the other is a zero-pole-gain model, the resulting model is a state-space model. To access and modify the data in the model, use the Model Information VIs. |
 |
error out contains error information. This output provides standard error out functionality. |
CD Subtract Models (Gain from Zero-Pole-Gain)

 |
Model In specifies the model from which you want to subtract information. |
 |
Gain specifies the gain to subtract from the model. |
 |
error in describes error conditions that occur before this node runs. This input provides standard error in functionality. |
 |
Model Out returns the model this VI produces. When the two input models are not of the same model type, the following model hierarchy determines the model type of the resulting model: state-space>transfer function>zero-pole-gain. For example, if one input is a state-space model and the other is a zero-pole-gain model, the resulting model is a state-space model. To access and modify the data in the model, use the Model Information VIs. |
 |
error out contains error information. This output provides standard error out functionality. |
CD Subtract Models (Zero-Pole-Gain from Gain)

 |
Gain specifies the gain from which this VI subtracts the model. |
 |
Model In specifies the model this VI subtracts from the gain. |
 |
error in describes error conditions that occur before this node runs. This input provides standard error in functionality. |
 |
Model Out returns the model this VI produces. When the two input models are not of the same model type, the following model hierarchy determines the model type of the resulting model: state-space>transfer function>zero-pole-gain. For example, if one input is a state-space model and the other is a zero-pole-gain model, the resulting model is a state-space model. To access and modify the data in the model, use the Model Information VIs. |
 |
error out contains error information. This output provides standard error out functionality. |
CD Subtract Models Details
Model 1, Model 2, and Model Out are of the same type and have the same number of inputs and outputs. Therefore, this operation is equivalent to a parallel connection of models that share the same set of inputs, and whose outputs are subtracted accordingly.
This VI might convert one or both input models to different forms before connecting the models. Refer to the LabVIEW Control Design User Manual for more information about appending models.
This VI supports delays. This VI transfers the delay information from the input models to the augmented model. Refer to the LabVIEW Control Design User Manual for more information about delays.