Jacobian Elliptic Functions VI
- Updated2025-07-30
- 2 minute(s) read
Determines the Jacobian elliptic functions cn, dn, and sn.
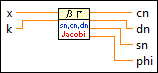
Inputs/Outputs
 x
—
x
—
x is the input argument. If x is negative, the VI uses the absolute value of x.  k
—
k
—
k is the integrand parameter.  cn
—
cn
—
cn returns the value of the Jacobi elliptic function cn.  dn
—
dn
—
dn returns the Jacobi elliptic function dn.  sn
—
sn
—
sn returns the value of the Jacobi elliptic function sn.  phi
—
phi
—
phi is the upper limit of the integral defining the function. |
The following equations define the three Jacobian elliptic functions.
cn(x, k) = cos(ϕ) sn(x, k) = sin(ϕ)
where

The function is defined according to the following intervals for the input values.

For any real value of integrand parameter k in the unit interval, the function is defined for all real values of x.