Evaluate Classification Model VI
- Updated2023-02-21
- 4 minute(s) read
Evaluate Classification Model VI
Owning Palette: Classification VIs
Requires: Analytics and Machine Learning Toolkit
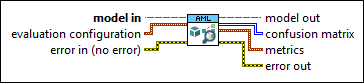
Evaluates a trained classification model by using new test data with labels.
You must load the new test data by using the Deployment instance of the Load Data (2D Array) VI.
 |
model in specifies the information about the entire workflow of the model. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 |
evaluation configuration specifies the configuration for the evaluation metric.
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 |
error in describes error conditions that occur before this node runs. This input provides standard error in functionality. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 |
model out returns the information about the entire workflow of the model. Wire model out to the reference input of a standard Property Node to get an AML Analytics Property Node. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 |
confusion matrix returns the confusion matrix from the evaluation result. A confusion matrix describes the performance of a classification model by reporting the number of true positive cases, true negative cases, false positive cases, and false negative cases. Each row of a confusion matrix represents the actual class and each column represents the predicted class.
For example, for 100 samples, there are two possible classes: positive and negative. The following table is a confusion matrix for the two classes.
The confusion matrix contains 65 true positive cases, 5 false negative cases, 19 false positive cases, and 11 true negative cases. |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 |
metrics returns metrics from the evaluation result.
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 |
error out contains error information. This output provides standard error out functionality. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Example
Refer to the Classification (Deployment) VI in the labview\examples\AML\Classification directory for an example of using the Evaluate Classification Model VI.






