WA WP Decomposition VI
- Updated2023-02-21
- 10 minute(s) read
WA WP Decomposition VI
Owning Palette: Wavelet Packet VIs
Requires: Advanced Signal Processing Toolkit
Computes the 1D wavelet packet (WP) decomposition and stores the resulting coefficients and wavelet packet tree information in the wavelet packet structure. Wire data to the signal input to determine the polymorphic instance to use or manually select the instance.
WA WP Decomposition (Waveform)

 |
entropy specifies the method and the associated parameter to use to compute the entropy of the wavelet packet coefficients.
| ||||||||||||||
 |
extension specifies the method to use to pad data at the borders of the input signal. The extension length is equal to the length of the wavelet filters. When you select the extension method, make the transition between the input signal and the padded data as smooth as possible because a smooth transition generates fewer large detail coefficients and enhances the efficiency of the signal representation.
|
||||||||||||||
 |
WP session specifies a reference to an existing wavelet packet structure. | ||||||||||||||
 |
signal specifies the input signal. | ||||||||||||||
 |
levels specifies the number of levels in the discrete wavelet analysis. levels must be a positive integer no greater than log2(Ls), where Ls is the length of the signal. Otherwise, you can set the value to –1, which indicates that this VI sets levels as the largest integer no greater than log2(Ls). The default is –1. | ||||||||||||||
 |
error in describes error conditions that occur before this node runs. This input provides standard error in functionality. | ||||||||||||||
 |
wavelet specifies the wavelet type to use for the discrete wavelet analysis. The default is db02. The options include two types: orthogonal (Haar, Daubechies (dbxx), Coiflets (coifx), Symmlets (symx)) and biorthogonal (Biorthogonal (biorx_x), including FBI (bior4_4 (FBI))), where x indicates the order of the wavelet. The higher the order, the smoother the wavelet. The orthogonal wavelets are not redundant and are suitable for signal or image denoising and compression. The biorthogonal wavelets usually have the linear phase property and are suitable for signal or image feature extraction. If you want to use other types of wavelets, do not wire this input. Instead, use the Wavelet Design Express VI to design the wavelet you want, bundle the resulting analysis and synthesis filters, and then wire them to the filter banks input. | ||||||||||||||
 |
filter banks specifies the analysis filter banks and the synthesis filter banks for the wavelet you specify. If you specify a value for filter banks, this VI ignores the settings in the wavelet input. You can use the Wavelet Design Express VI to design the analysis filters and the corresponding synthesis filters.
| ||||||||||||||
 |
WP session out returns a reference to an existing wavelet packet structure, which this VI can modify. | ||||||||||||||
 |
error out contains error information. This output provides standard error out functionality. |
WA WP Decomposition (Array)
 |
entropy specifies the method and the associated parameter to use to compute the entropy of the wavelet packet coefficients.
| ||||||||||||||
 |
extension specifies the method to use to pad data at the borders of the input signal. The extension length is equal to the length of the wavelet filters. When you select the extension method, make the transition between the input signal and the padded data as smooth as possible because a smooth transition generates fewer large detail coefficients and enhances the efficiency of the signal representation.
|
||||||||||||||
 |
WP session specifies a reference to an existing wavelet packet structure. | ||||||||||||||
 |
signal specifies the input signal. | ||||||||||||||
 |
levels specifies the number of levels in the discrete wavelet analysis. levels must be a positive integer no greater than log2(Ls), where Ls is the length of the signal. Otherwise, you can set the value to –1, which indicates that this VI sets levels as the largest integer no greater than log2(Ls). The default is –1. | ||||||||||||||
 |
error in describes error conditions that occur before this node runs. This input provides standard error in functionality. | ||||||||||||||
 |
wavelet specifies the wavelet type to use for the discrete wavelet analysis. The default is db02. The options include two types: orthogonal (Haar, Daubechies (dbxx), Coiflets (coifx), Symmlets (symx)) and biorthogonal (Biorthogonal (biorx_x), including FBI (bior4_4 (FBI))), where x indicates the order of the wavelet. The higher the order, the smoother the wavelet. The orthogonal wavelets are not redundant and are suitable for signal or image denoising and compression. The biorthogonal wavelets usually have the linear phase property and are suitable for signal or image feature extraction. If you want to use other types of wavelets, do not wire this input. Instead, use the Wavelet Design Express VI to design the wavelet you want, bundle the resulting analysis and synthesis filters, and then wire them to the filter banks input. | ||||||||||||||
 |
filter banks specifies the analysis filter banks and the synthesis filter banks for the wavelet you specify. If you specify a value for filter banks, this VI ignores the settings in the wavelet input. You can use the Wavelet Design Express VI to design the analysis filters and the corresponding synthesis filters.
| ||||||||||||||
 |
WP session out returns a reference to an existing wavelet packet structure, which this VI can modify. | ||||||||||||||
 |
error out contains error information. This output provides standard error out functionality. |
WA WP Decomposition Details
The following illustration shows a full decomposition of the wavelet packet tree at level 3:
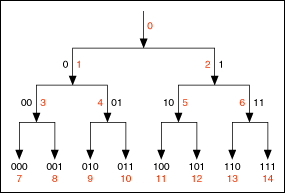
The black numbers indicate the path of each node, and the red numbers show the index of each node. The path is a combination of the characters 0 and 1, where 0 represents lowpass filtering, and 1 represents highpass filtering. For example, a value of 101 indicates that this VI passes the signal through a highpass filter, through a lowpass filter, and then through a highpass filter.
The discrete wavelet decomposition and the arbitrary path decomposition are two special cases of the wavelet packet decomposition. You can decompose the approximation coefficients and the detail coefficients in the wavelet packet decomposition. The discrete wavelet decomposition implements the analysis filtering only on the approximation coefficients. However, you can apply analysis filtering to the approximation or the detail in the arbitrary path decomposition.
Examples
Refer to the following VIs for examples of using the WA WP Decomposition VI:
- Wavelet Packet - Plot Tree VI: labview\examples\Wavelet Analysis\WAGettingStarted
- Wavelet Packet - Read and Write Coefficients VI: labview\examples\Wavelet Analysis\WAGettingStarted
- Wavelet Packet - Read Entropy VI: labview\examples\Wavelet Analysis\WAGettingStarted
- Wavelet Packet - Join Node VI: labview\examples\Wavelet Analysis\WAGettingStarted
- Wavelet Packet - Split Node VI: labview\examples\Wavelet Analysis\WAGettingStarted
- Wavelet Packet Signal Compression VI: labview\examples\Wavelet Analysis\WAApplications
