SI Estimate FRF VI
- Updated2023-02-21
- 16 minute(s) read
SI Estimate FRF VI
Owning Palette: Frequency-Domain Model Estimation VIs
Requires: Advanced Signal Processing Toolkit or Control Design and Simulation Module
Estimates the frequency response function (FRF) of an unknown system. Use the FRF to estimate a transfer function (TF) model or a state-space (SS) model of the system.
Wire data to the stimulus signal and response signal inputs to determine the polymorphic instance to use or manually select the instance.
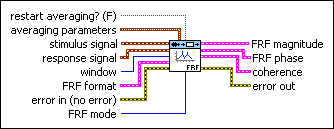
SI Estimate FRF (SISO Waveform)
 |
restart averaging? specifies whether to restart the averaging process. The default is FALSE. When you call this VI for the first time, the averaging process restarts automatically. You might need to restart averaging if a major input change occurs in the middle of the averaging process. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 |
averaging parameters specifies how this VI computes the averaged FRF.
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 |
stimulus signal specifies the input waveform of the stimulus signal. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 |
response signal specifies the input waveform of the response signal. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 |
window specifies the time-domain window to apply to the stimulus signal and response signal.
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 |
FRF format specifies the format of the FRF magnitude and the FRF phase.
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 |
error in describes error conditions that occur before this node runs. This input provides standard error in functionality. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 |
FRF mode specifies how this VI computes the frequency response function (FRF). The mode you choose depends on the signal(s) that contain noise.
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 |
FRF magnitude returns the magnitude of the averaged frequency response and frequency scale.
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 |
FRF phase returns the phase of the averaged frequency response and frequency scale.
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 |
coherence returns the coherence and the frequency scale of the FRF.
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 |
error out contains error information. This output provides standard error out functionality. |
SI Estimate FRF (SISO Array)

 |
restart averaging? specifies whether to restart the averaging process. The default is FALSE. When you call this VI for the first time, the averaging process restarts automatically. You might need to restart averaging if a major input change occurs in the middle of the averaging process. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 |
averaging parameters specifies how this VI computes the averaged FRF.
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 |
stimulus signal specifies an array that represents the stimulus signal. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 |
response signal specifies an array that represents the response signal. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 |
window specifies the time-domain window to apply to the stimulus signal and response signal.
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 |
FRF format specifies the format of the FRF magnitude and the FRF phase.
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 |
error in describes error conditions that occur before this node runs. This input provides standard error in functionality. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 |
sampling rate (Hz) specifies the sampling frequency in hertz. The value of sampling rate must be greater than 0. The default is 1. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 |
FRF mode specifies how this VI computes the frequency response function (FRF). The mode you choose depends on the signal(s) that contain noise.
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 |
FRF magnitude returns the magnitude of the averaged frequency response and frequency scale.
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 |
FRF phase returns the phase of the averaged frequency response and frequency scale.
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 |
coherence returns the coherence and the frequency scale of the FRF.
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 |
error out contains error information. This output provides standard error out functionality. |
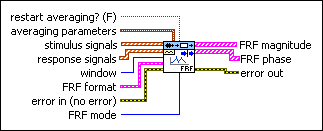
SI Estimate FRF (MIMO Waveform)
 |
restart averaging? specifies whether to restart the averaging process. The default is FALSE. When you call this VI for the first time, the averaging process restarts automatically. You might need to restart averaging if a major input change occurs in the middle of the averaging process. | ||||||||||||||||
 |
averaging parameters specifies how to compute the averaging process.
| ||||||||||||||||
 |
stimulus signals specifies the input waveform array of the stimulus signals. Each element of the array is the waveform of one stimulus signal. | ||||||||||||||||
 |
response signals specifies the input waveform array of the response signals. Each element of the array is the waveform of one response signal. | ||||||||||||||||
 |
window specifies the time-domain window to apply to the stimulus signals and response signals.
|
||||||||||||||||
 |
FRF format specifies the format of the FRF magnitude and the FRF phase.
| ||||||||||||||||
 |
error in describes error conditions that occur before this node runs. This input provides standard error in functionality. | ||||||||||||||||
 |
FRF mode specifies how this VI computers the frequency response function (FRF). If you know that noise contaminates the input or output signals of the unknown system, you can select the mode this VI uses to compute the FRF to minimize the measurement error.
|
||||||||||||||||
 |
FRF magnitude returns the magnitude of the averaged frequency response and frequency scale.
| ||||||||||||||||
 |
FRF phase specifies the phase of the averaged frequency response and frequency scale.
| ||||||||||||||||
 |
error out contains error information. This output provides standard error out functionality. |
SI Estimate FRF (MIMO Array)

 |
restart averaging? specifies whether to restart the averaging process. The default is FALSE. When you call this VI for the first time, the averaging process restarts automatically. You might need to restart averaging if a major input change occurs in the middle of the averaging process. | ||||||||||||||||
 |
averaging parameters specifies how to compute the averaging process.
| ||||||||||||||||
 |
stimulus signals specifies an array that represents the stimulus signals. Each row in the array is one stimulus signal. | ||||||||||||||||
 |
response signals specifies an array that represents the response signals. Each row in the array is one response signal. | ||||||||||||||||
 |
window specifies the time-domain window to apply to the stimulus signals and response signals.
|
||||||||||||||||
 |
FRF format specifies the format of the FRF magnitude and the FRF phase.
| ||||||||||||||||
 |
error in describes error conditions that occur before this node runs. This input provides standard error in functionality. | ||||||||||||||||
 |
sampling rate (Hz) specifies the sampling frequency in hertz. The value of sampling rate must be greater than 0. The default is 1. | ||||||||||||||||
 |
FRF mode specifies how this VI computers the frequency response function (FRF). If you know that noise contaminates the input or output signals of the unknown system, you can select the mode this VI uses to compute the FRF to minimize the measurement error.
|
||||||||||||||||
 |
FRF magnitude returns the magnitude of the averaged frequency response and frequency scale.
| ||||||||||||||||
 |
FRF phase specifies the phase of the averaged frequency response and frequency scale.
| ||||||||||||||||
 |
error out contains error information. This output provides standard error out functionality. |