RJ PJ Separation VI
- Updated2023-02-21
- 6 minute(s) read
RJ PJ Separation VI
Owning Palette: Jitter VIs
Requires: Jitter Analysis Toolkit
Separates the random and periodic components of jitter in a jitter sequence and returns their RMS and peak-to-peak values.
Refer to the Details section of this topic for more information about random and periodic jitter.
nTone
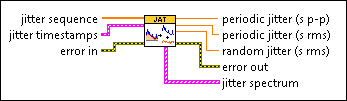
After this instance resamples the jitter sequence, as described in the Details section, it computes periodic jitter by modeling spectrum peaks as sinusoids and returning the sum of the identified sinusoids. This instance searches for peaks above a threshold within the amplitude spectrum of the jitter sequence.

 |
mode specifies how this VI identifies periodic jitter.
|
||||||
 |
jitter sequence is an array of jitter measurements. | ||||||
 |
jitter timestamps describes the waveform and the times at which measurements in the corresponding sequence occur.
| ||||||
 |
periodic fit settings contains the following elements that determine how this VI identifies periodic jitter.
| ||||||
 |
error in describes error conditions that occur before this node runs. This input provides standard error in functionality. | ||||||
 |
periodic search info returns the following elements that describe the periodic jitter in the jitter sequence.
| ||||||
 |
periodic jitter (s p-p) returns the periodic jitter measured as a peak-to-peak value. | ||||||
 |
periodic jitter (s rms) returns the standard deviation of the periodic jitter in the jitter sequence. | ||||||
 |
random jitter (s rms) returns the RMS value of the original jitter sequence minus the periodic jitter. | ||||||
 |
error out contains error information. This output provides standard error out functionality. | ||||||
 |
jitter spectrum is a graph that displays the spectrum of the original jitter sequence and the periodic jitter in the signal. |
Spectral Trend
After this instance resamples the jitter sequence, as described in the Details section, it removes the DC level and then computes the power spectrum. This instance approximates and removes the spectrum trend and peaks, leaving the random portion of the spectrum.
 |
jitter sequence is an array of jitter measurements. | ||||||
 |
jitter timestamps describes the waveform and the times at which measurements in the corresponding sequence occur.
| ||||||
 |
error in describes error conditions that occur before this node runs. This input provides standard error in functionality. | ||||||
 |
periodic jitter (s p-p) returns the periodic jitter measured as a peak-to-peak value. | ||||||
 |
periodic jitter (s rms) returns the standard deviation of the periodic jitter in the jitter sequence. | ||||||
 |
random jitter (s rms) returns the RMS value of the original jitter sequence minus the periodic jitter. | ||||||
 |
error out contains error information. This output provides standard error out functionality. | ||||||
 |
jitter spectrum is a graph that displays the spectrum of the original jitter sequence and the periodic jitter in the signal. |
RJ PJ Separation Details
If you wire waveform data to the jitter timestamps input, this VI resamples the input jitter sequence so it is evenly sampled. Otherwise, this VI assumes the measurements in the jitter sequence are already evenly sampled. Jitter sequences are not evenly sampled in time because the jitter is measured when the last value required to measure the jitter occurs. For example, time interval error values have corresponding timestamps at the level crossing of the data signal, while period jitter values have corresponding timestamps at the time of the second level crossing of the data signal. Thus, the resampling allows the jitter sequence to be evenly spaced for the FFT.
Random Jitter vs. Periodic Jitter
Random jitter is unbounded and does not achieve a maximum or minimum phase deviation within any time interval. By contrast, deterministic jitter is bounded and reaches maximum and minimum phase deviation values within an identifiable time interval. Periodic jitter is a type of systematic deterministic jitter that is not data dependent, or correlated with a specific sequence of bits in a waveform.
Examples
Refer to the following VIs for examples of using the RJ PJ Separation VI:
- Rj Dj Separation VI: labview\examples\Jitter Analysis\Jitter Measurements
- Rj Dj Delta Delta Separation VI: labview\examples\Jitter Analysis\Jitter Measurements



