Find All Zeros of f(x) (Formula) VI
- Updated2025-07-30
- 3 minute(s) read
Determines all zeros of a 1D function in a given interval. You must manually select the polymorphic instance to use.

Inputs/Outputs
 accuracy
—
accuracy
—
accuracy controls the accuracy of the zeros and the extrema. The default is 1.00E-8.  step type
—
step type
—
step type controls the spacing used for the function values. In general, modified function leads to more accurate zeros and extrema.
 algorithm
—
algorithm
—
algorithm is the method used by the VI.
 start
—
start
—
start is the start point of the interval. The default is 0.0.  end
—
end
—
end is the end point of the interval. The default is 1.0.  formula
—
formula
—
formula is a string describing the function. The formula can contain any number of valid variables.  Zeros
—
Zeros
—
Zeros are the determined zeros of formula.  f(Zeros)
—
f(Zeros)
—
f(Zeros) contains the function values of Zeros. Usually, these values are close to 0.  ticks
—
ticks
—
ticks is the time in milliseconds for the whole calculation.  error
—
error
—
error returns any error or warning from the VI. You can wire error to the Error Cluster From Error Code VI to convert the error code or warning into an error cluster. |
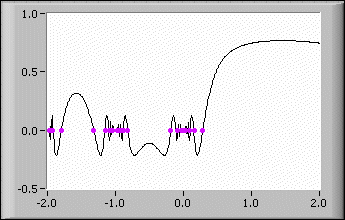
To obtain the zeros of sin(sinc(gamma(x))) in the interval (–2, 2), enter the following values on the front panel:
- start: -2.00
- end: 2.00
- formula: sin(sinc(gamma(x)))
The following illustration shows the graph and the zeros of sin(sinc(gamma(x))) in the interval (–2, 2).
Examples
Refer to the following example files included with LabVIEW.
- labview\examples\Mathematics\Optimization\1D Explorer.vi